 Laparoscopy in Infertility: Diagnosis and Treatment
Laparoscopy in Infertility: Diagnosis and Treatment
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure used in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope, a thin fiber-optic tube with a light and camera, is inserted. This allows the doctor to view the abdominal organs and perform surgical interventions without the need for a large incision.
When is Laparoscopy Used?
Laparoscopy may be recommended for the following reasons:
- Diagnostic Purposes: To investigate the cause of infertility, especially when other tests such as hysterosalpingography have been inconclusive.
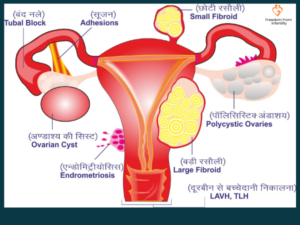
- Treatment of Fertility Problems: To address specific issues that may be affecting fertility, such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), blocked fallopian tubes, ovarian cysts, or fibroids.
- Pelvic Pain: Laparoscopy may be recommended if you experience pelvic pain during intercourse or at other times in your cycle.
- Suspected Endometriosis: For the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes: To assess and potentially open blocked fallopian tubes, which can hinder the egg’s journey to the uterus.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: To detect and manage ectopic pregnancies, which occur when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
- Severe Menstrual Cramps: Laparoscopy may be used to investigate and treat severe menstrual cramps that are not responsive to other treatments.
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy: Used to visualize and evaluate the pelvic organs for any abnormalities or conditions that may be contributing to infertility.
- Therapeutic Laparoscopy: Involves surgical interventions to treat identified issues, such as removing scar tissue, cysts, fibroids, or repairing fallopian tubes.
- Hospital Setting: Laparoscopy is typically performed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
- Small Incisions: One or more small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Carbon Dioxide Gas: The abdomen is filled with carbon dioxide gas to create space for better visualization of the organs.
- Evaluation and Treatment: The surgeon examines the pelvic organs, looking for abnormalities, adhesions, cysts, or endometrial growths. Any identified issues may be treated during the same procedure.
- Post-Surgery: Patients may experience soreness, bloating, and shoulder pain from the gas used during surgery.
- Pain Management: Pain medications and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage discomfort and prevent infection.
- Follow-up: Patients are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a few days. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor recovery and discuss further steps.
- Common Risks: Bladder infection, skin irritation, and minor complications are possible.
- Less Common Risks: Adhesions, hematomas, infection, and allergic reactions.
- Serious Complications: Organ or blood vessel damage, nerve damage, blood clots, and anesthesia-related risks.
- Treatment Outcomes: The success of laparoscopy in improving fertility depends on the underlying condition and the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Enhanced Fertility: Removal of obstructions, such as adhesions or blocked tubes, may improve the chances of natural conception.
- Fertility Treatments: After recovery, patients may consider fertility treatments if pregnancy does not occur naturally.
For expert laparoscopic procedures and personalized fertility care, consult with the experienced team at Jindal Hospital & Fertility Centre, led by renowned experts in the field of reproductive medicine, Dr. Sunil Jindal and Dr. Anshu Jindal. We use world class state of the art equipment and our expertise goes far beyond normal fertility laparoscopy. As one of the best fertility centres, Jindal Hospital offers advanced laparoscopic techniques for the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, ensuring comprehensive care and improved fertility outcomes.
Laparoscopy is often recommended for infertility cases, especially when women have unexplained infertility despite normal results from other fertility tests. It is also advised to investigate the cause of any abdominal pain or discomfort that may be related to fertility issues.
Diagnostic Uses of Laparoscopy in Infertility:
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes (Hydrosalpinx): Laparoscopy helps identify and treat blockages in the fallopian tubes, which can hinder the egg’s journey to the uterus.
- Scar Tissue and Adhesions: The procedure allows doctors to detect and remove scar tissue or adhesions that may be affecting the reproductive organs’ function.
- Endometriosis: Laparoscopy is crucial in diagnosing and treating endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus.
- Fibroids and Ovarian Cysts: It helps in identifying and addressing fibroids or ovarian cysts that could impact fertility.
- Other Anatomical Abnormalities: Laparoscopy enables the examination of the reproductive system for any other structural abnormalities that may be contributing to infertility.
Benefits of Laparoscopy for Infertility:
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Laparoscopy allows doctors to both diagnose and treat the underlying causes of infertility in one procedure.
- Removal of Anomalies: If abnormalities are found during laparoscopy, such as scar tissue or fibroids, they can be removed, improving the chances of natural conception.
- Biopsy for Suspicious Growth: In cases of suspicious growths or tissues, a biopsy can be taken during the procedure for further evaluation.
- Improving IVF Success: Treating conditions like endometriosis or hydrosalpinx through laparoscopy can significantly enhance the success rates of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) procedures.
Procedure and Recovery:
- Hospital Setting: Laparoscopy is typically performed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
- Small Incisions: The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: The laparoscope allows for a thorough examination of the pelvic organs to identify any abnormalities.
- Surgical Intervention: If abnormalities are detected, the surgeon can perform procedures such as removing scar tissue, cysts, or fibroids.
- Recovery: Patients may experience mild discomfort, bloating, or shoulder pain from the procedure, but recovery is generally quick, and most patients can go home the same day.
Enhancing Fertility Outcomes:
- Natural Conception: By addressing and correcting underlying issues, laparoscopy improves the chances of natural conception.
- Increased IVF Success: Removing obstacles like endometriosis or hydrosalpinx enhances the success rates of assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF.
Expert Care at Jindal Hospital & Fertility Centre:
For comprehensive laparoscopic procedures and personalized fertility care, Jindal Hospital & Fertility Centre offers advanced treatment options under the guidance of renowned experts, Dr. Sunil Jindal and Dr. Anshu Jindal. As a leading fertility centre, Jindal Hospital provides cutting-edge laparoscopic techniques to diagnose and treat infertility, with a focus on improving fertility outcomes and helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood.
Laparoscopy Surgery Procedure: A Minimally Invasive Approach
Laparoscopy surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a relatively straightforward procedure performed under general anesthesia. Here’s what you can expect during and after the surgery: Procedure Overview:- Anesthesia: You will receive general anesthesia before the surgery begins to ensure you are comfortable and pain-free.
- Gas Injection: Once under anesthesia, the surgeon will make a small incision near your navel and insert a needle to inject gas into your abdomen. This gas helps to inflate the abdomen, creating space to view the organs clearly.
- Insertion of Laparoscope: Next, a laparoscope—a thin, lighted tube with a camera—is inserted through the incision. This allows the surgeon to examine your abdominal organs and structures on a monitor.
- Diagnostic Examination: The surgeon carefully examines the organs and identifies any abnormalities or conditions that may require further attention.
Surgical Intervention (If Needed):
- Additional Incisions: If the surgeon identifies an anomaly that requires surgical intervention, one or more small incisions may be made to accommodate specialized surgical instruments.
- Procedure Completion: The necessary surgical procedure, such as removing scar tissue, cysts, or repairing abnormalities, is performed through these additional incisions.
- Closure of Incisions: Once the surgery is complete, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Post-Surgery Recovery:
- Observation Period: After the procedure, you will be monitored in a recovery area for a few hours to ensure there are no immediate complications.
- Discomfort and Pain: It is common to experience some discomfort and mild pain following laparoscopy. You may also feel pain in your shoulders and abdomen due to the residual gas in your abdomen.
- Symptom Relief: Your doctor will provide medication to help manage any pain or discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended.
- Short Recovery Time: Compared to traditional open surgeries, the recovery time for laparoscopy is typically much shorter.
- Returning to Normal Activities: Most patients can resume their normal activities within a few days of the surgery, although strenuous activities should be avoided for a bit longer.
- Follow-Up Care: Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-operative care, including any dietary restrictions, wound care, and when to follow up for a check-up.
Possible Side Effects and Complications:
- Minor Risks: While laparoscopy is generally safe, there are some minor risks associated with the procedure.
- Rare Complications: About 1% to 2% of patients may experience complications such as bladder infections, adhesions (scar tissue), infections at the incision sites, or hematomas (collections of blood) in the abdominal wall.
- Prompt Reporting: It’s important to report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your doctor promptly for appropriate management.
Enhanced Recovery and Comfort:
- Minimally Invasive Benefits: Laparoscopy offers numerous advantages, including smaller incisions, reduced risk of infection, less post-operative pain, and quicker recovery.
- Effective Treatment: The procedure allows for effective diagnosis and treatment of various gynecological conditions with minimal disruption to normal activities.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, laparoscopy surgery is a safe and effective minimally invasive procedure for diagnosing and treating a range of gynecological issues. With proper post-operative care and follow-up, patients can expect a speedy recovery and a return to their daily routines. For laparoscopy surgery performed with expertise and personalized care, Jindal Hospital & Fertility Centre, under the guidance of renowned doctors Dr. Sunil Jindal and Dr. Anshu Jindal, provides comprehensive treatment options for patients seeking fertility solutions.
The Do’s and Don’ts of Laparoscopy in Infertility
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating infertility in both men and women. As with any medical procedure, there are certain do’s and don’ts associated with laparoscopy to ensure optimal outcomes and a smooth recovery process. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essential guidelines for patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures for infertility treatment.
The Do’s of Laparoscopy in Infertility
1. Choose a Skilled Surgeon
The success of laparoscopic surgery heavily relies on the expertise of the surgeon. Patients should seek out a board-certified doctor with significant experience in performing laparoscopic procedures for infertility.
2. Undergo Preoperative Testing
Before the surgery, patients should complete all necessary preoperative testing as recommended by their doctor. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostic evaluations to ensure they are in optimal health for the procedure.
3. Follow Preoperative Instructions
It is crucial to adhere to any preoperative instructions provided by the doctor. This may involve fasting for a certain period, stopping specific medications, or preparing the body in other ways to enhance the success of the surgery.
4. Discuss All Concerns
Patients should openly discuss any concerns or questions with their doctor before the procedure. Doctors are there to provide clarity, address fears, and ensure that patients feel comfortable and informed.
5. Prepare for Recovery
Before undergoing laparoscopy, patients should arrange for someone to drive them home from the hospital or surgical center. It is also essential to have a designated caregiver to assist with daily tasks during the initial days of recovery.
6. Follow Postoperative Care Instructions
After the surgery, patients must diligently follow all postoperative care instructions provided by their doctor. This includes taking prescribed medications, attending follow-up appointments, and following specific guidelines for activity and rest.
The Don’ts of Laparoscopy in Infertility
1. Don’t Ignore Preoperative Guidelines
Ignoring preoperative guidelines, such as fasting requirements or medication restrictions, can increase the risk of complications during surgery. Patients should strictly adhere to all instructions provided by their doctor.
2. Avoid Strenuous Activities
In the days following laparoscopy, patients should refrain from engaging in strenuous activities or heavy lifting. Overexertion can lead to discomfort, delayed healing, and potential complications.
3. Don’t Drive Immediately After Surgery
Driving after laparoscopy is not recommended, as the effects of anesthesia and the surgical procedure itself can impair patients’ ability to operate a vehicle safely. It is crucial to have a designated driver for the journey home.
4. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Both smoking and alcohol consumption can interfere with the body’s healing process and increase the risk of complications. Patients should refrain from smoking and limit alcohol intake before and after laparoscopy.
5. Don’t Neglect Follow-up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are vital for monitoring patients’ recovery progress, addressing any concerns, and ensuring that the surgery was successful. Skipping these appointments can hinder patients’ recovery and overall outcomes.
6. Avoid Tight Clothing
Wearing tight clothing, especially around the abdominal area, can cause discomfort and interfere with the healing process. Patients should opt for loose, comfortable clothing during the initial days of recovery.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Successful Laparoscopic Procedure
In conclusion, laparoscopy is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility. By following the do’s and don’ts outlined in this guide, patients can optimize the success of their laparoscopic procedure and promote a smooth recovery process.
10 FAQ About Laparoscopy in Infertility
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating infertility issues in both men and women. Here are 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) about laparoscopy in infertility:
1. What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope. This allows doctors to view the internal organs, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus, on a monitor.
2. How Does Laparoscopy Help in Infertility?
Laparoscopy helps doctors diagnose and treat various causes of infertility, such as:
- Endometriosis
- Blocked fallopian tubes
- Uterine fibroids
- Ovarian cysts
- Pelvic adhesions
3. Is Laparoscopy Painful?
Patients undergoing laparoscopy are usually under general anesthesia, so they do not feel pain during the procedure. Some mild discomfort or bloating may occur afterward, but this can be managed with medication.
4. What Are the Benefits of Laparoscopy?
The benefits of laparoscopy in infertility include:
- Minimally invasive with smaller incisions
- Quicker recovery time compared to traditional surgery
- Reduced risk of infection and complications
- Improved accuracy in diagnosis and treatment
5. How Long Does Laparoscopy Take?
The duration of a laparoscopy procedure varies depending on the complexity of the case. On average, it takes about 30 minutes to 3 hour.
6. What Can I Expect During Recovery?
Patients can typically go home the same day as the procedure or after a short observation period. Recovery time varies, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few days to a week.
7. Are There Any Risks or Complications?
While laparoscopy is generally safe, like any surgical procedure, there are some risks, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Damage to nearby organs
- Reaction to anesthesia
8. Can Laparoscopy Improve Fertility?
Yes, laparoscopy can improve fertility by addressing underlying issues that may be causing infertility. For example, removing endometriosis or unblocking fallopian tubes can increase the chances of conception. It is complimentary to assisted reproductive technology.
9. When is Laparoscopy Recommended?
Doctors may recommend laparoscopy when:
- Initial fertility tests are inconclusive
- There is suspicion of endometriosis or other pelvic conditions
- Blocked fallopian tubes are suspected
- There is a need to remove fibroids or cysts
10. Is Laparoscopy Covered by Insurance?
In many cases, laparoscopy for infertility is covered by insurance, especially when it is deemed medically necessary. Patients should check with their insurance provider to understand coverage and any out-of-pocket expenses.
Conclusion
Laparoscopy plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating infertility, offering patients a minimally invasive and effective option. If you have further questions about laparoscopy or infertility treatments, it is best to consult with a fertility specialist.

